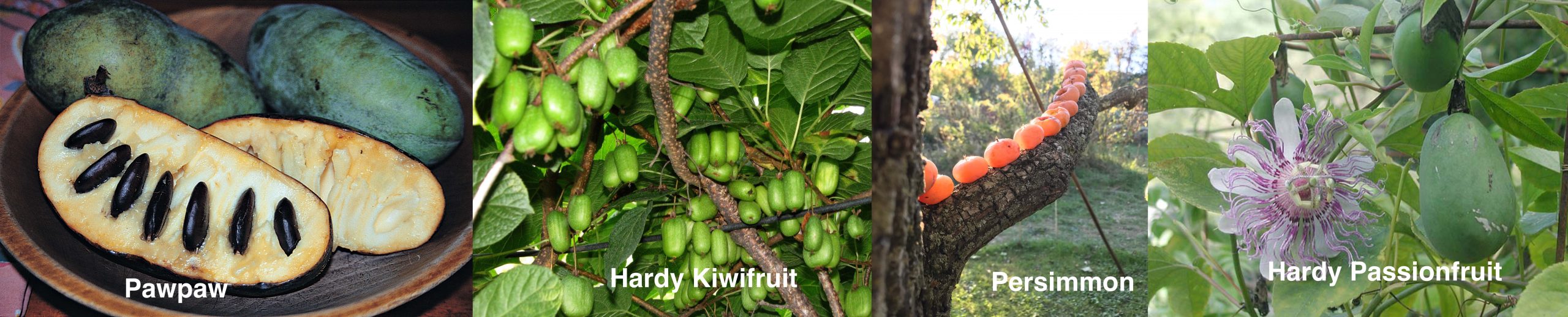
A DELECTABLE PEACH
A Time Machine
A few days ago, a fuzzy orb that I held in my hand became a time machine. This time machine was a peach, and time travel took place immediately after I took a bite out of it. There I was, no longer eating the peach on my friend Wendy’s farm — Wendy is a botanical artist, https://drawbotanical.com — but in the backyard of my youth, biting into a peach from our backyard tree. (Our home “orchard” also consisted of two crabapple trees, whose fruit was morphed under the direction of a great aunt into jelly, and a pear tree that I remember bearing only one fruit that I watched daily only to find it, one day, gone, picked prematurely by my sister.)

Back to the time machine peaches. These peaches would never sell at a supermarket, even a farmers’ market. Their skin was very fuzzy and a washed out yellow color, some with just a hint of a blush. I remember, when I worked for Cornell University Roger Way, the apple breeder at the time, bemoaning the fact that “Americans eat with their eyes.” Spots from peach scab disease on many of the fruits did nothing to increase their visual appeal.
“Would never sell,” that is, unless a taste was offered. Protected within that admittedly ugly skin was a meaty, golden yellow flesh. The flesh was sweet and, in contrast to most peaches these days, very rich-tasting, with a strong peachy flavor. It’s that peachy flavor that whisked me backwards in time.
I Make a New Peach Tree

Long gone peach
This year has been the best ever fruit year in decades around here, even right here on the farmden, where the low-lying site is not very fruit-friendly. Peaches always fail here; a few weeks ago I finally cut down my one tree. Twice over the past years I planted apricot trees, knowing that they are one of the fruits least likely to succeed around here. I was right; they are long gone.
Against my better judgement I am going to once again venture into peachdom. Perhaps Wendy’s peach is resistant to peach ills: brown rot, plum curculio, oriental fruit moth, bacterial spot, and peach scab. (Yes, her fruits were afflicted by scab, but not enough to diminish the pleasure of biting into them.)
Wendy isn’t sure of the variety name of her tree so I can’t order that one from a nursery. No matter.
Pits saved from some of the fruits can be grown into whole new trees. Seed-grown peach trees grow quickly and can take only three or four years before their branches are adorned by fruits. Plant a peach pit now, and it will not sprout until next spring, even if you keep it warm. Like other temperate-zone fruits, the seeds need to be stratified, that is, they must experience winter before they’ll sprout. If they sprouted now, the young, tender seedlings would succumb to winter cold.
Plant the pit outdoors, and it will be naturally stratified. I prefer to fool the pit by cracking the outer shell, soaking the seed in water for a few hours, then putting it in a plastic bag, along with moist potting soil, in the refrigerator. Refrigerator-stratified seeds sprout more quickly than outdoor planted seeds because once the outdoor-sown seeds have experienced enough cold, a total accumulation of about 1,000 hours of temperatures between 30 and 45 degrees Fahrenheit, they have to await spring warmth before they’ll grow.
Seeds stratified in the refrigerator will often sprout in the bag within a couple of months, at which point they need to be planted. I plan to pot them up and let them grow in the greenhouse.
Seed-grown fruit trees generally don’t bear fruit identical to the fruits from which the seeds came. It depends on what variety pollinated the flower that became the fruit, and how the chromosomes got juggled around. Peach trees are self-pollinating, which reduces the variability from fruit parent to fruit child, so there’s a good chance that a seed grown peach tree will yield tasty fruit. In contrast, plant an apple seed and there’s about one in 10,000 chance that the fruit from the resulting chance will even be edible.
If I wanted an exact replica of Wendy’s peach, I could beg a branch from her tree and graft it onto a peach rootstock. What’s a peach rootstock? It could be any peach tree grown from seed.
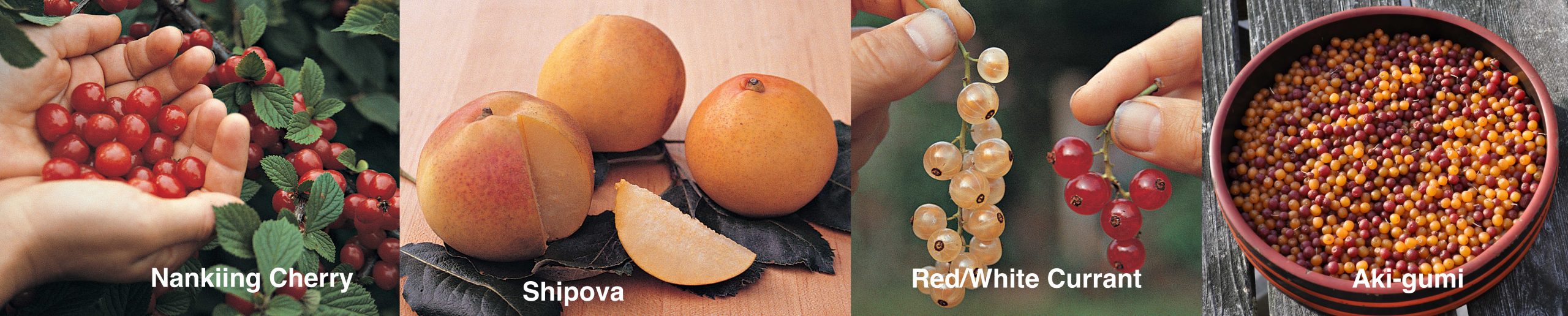
And Almonds!
Despite apricot’s strong nomination for the tree crop least like to succeed around here and, actually, pretty much everywhere in eastern North America, it does not win the prize. Almond trees are less likely to succeed. With that said, in this best of all years for fruit, here in the Northeast, at least, Wendy managed to harvest her first (and perhaps her only) crop of almonds this year.
Almonds are closely related to peaches. Their common ancestor diverged six million years ago with the separation resulting by the lifting of the Himalayan massif. Both plants suffer from the same insect and disease problems.
Two characteristics put almonds in the most likely to fail category. First, in humid climates, the nuts themselves are apt to spoil. And second, almonds have a very low chilling requirement. (Just as seeds have chilling requirements before they will sprout, flower and stem buds also have chilling requirements before they can sprout.) With a low chilling requirement, almonds would likely break dormancy and flower with the first hint of warm weather in spring, then succumb to likely subsequent frosts.
But not this year.
Needless to say, I will not be giving almonds a try on my farmden.
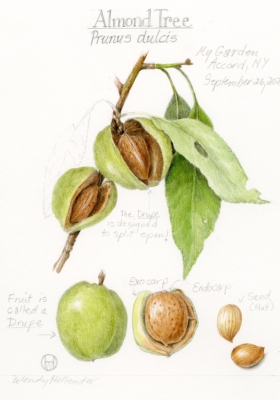
Almond illustration, by Wendy
















 If not harvested, the later crop hangs, looking pretty and in good condition for eating, through autumn and on into winter.
If not harvested, the later crop hangs, looking pretty and in good condition for eating, through autumn and on into winter.

























 Because I grow it mostly as an ornamental and because it grows right near one corner of my vegetable garden, I don’t want it to grow too large. Last year at about this time I decided to hedge its crown into a pleasing shape.
Because I grow it mostly as an ornamental and because it grows right near one corner of my vegetable garden, I don’t want it to grow too large. Last year at about this time I decided to hedge its crown into a pleasing shape.











 I’ve invited a few non-family members into the bed. Most notable are a witchhazel that’s covered in fragrant, yellow blossoms in late winter and a stewartia that is now spreading open the white petals of its camellia-like blossoms.
I’ve invited a few non-family members into the bed. Most notable are a witchhazel that’s covered in fragrant, yellow blossoms in late winter and a stewartia that is now spreading open the white petals of its camellia-like blossoms.






