Snow Mulching
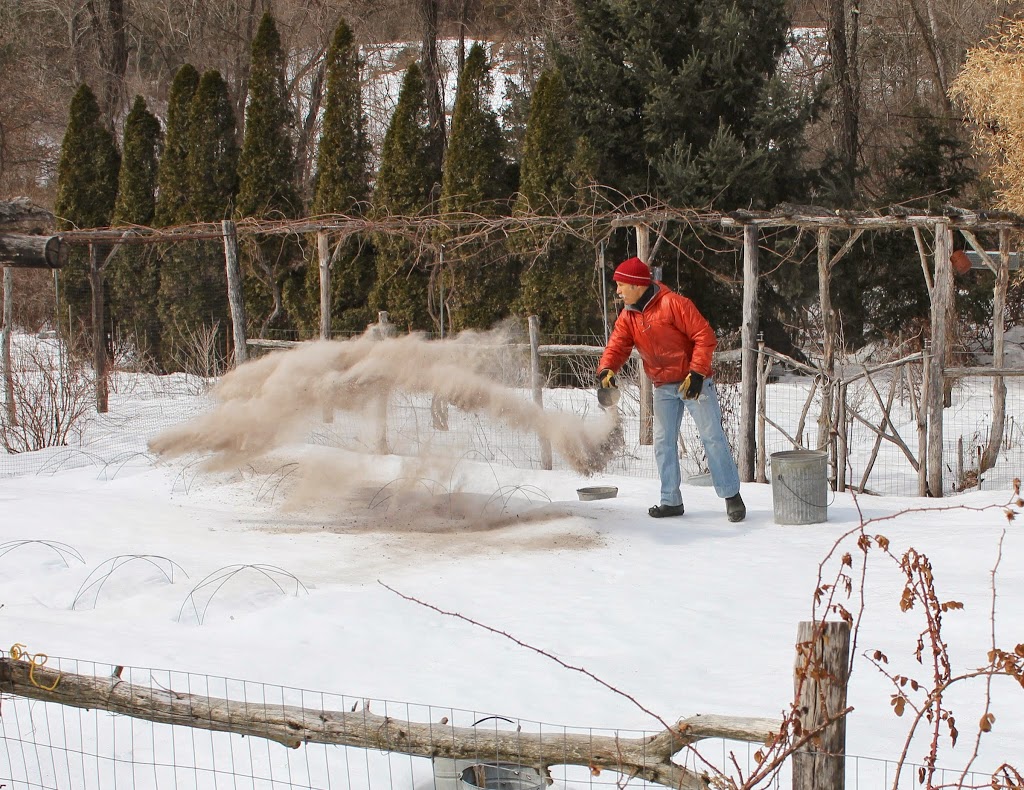
Only four inches of snow fell a a couple of weeks ago but I decided anyway to go outside and mulch. And shovel snow. And shovel snow and mulch.
What I was trying to do, besides clear snow from the driveway, the paths, and the doorway to the greenhouse, was to create a microclimate. A microclimate is a small area where the climate is slightly different from the general climate.
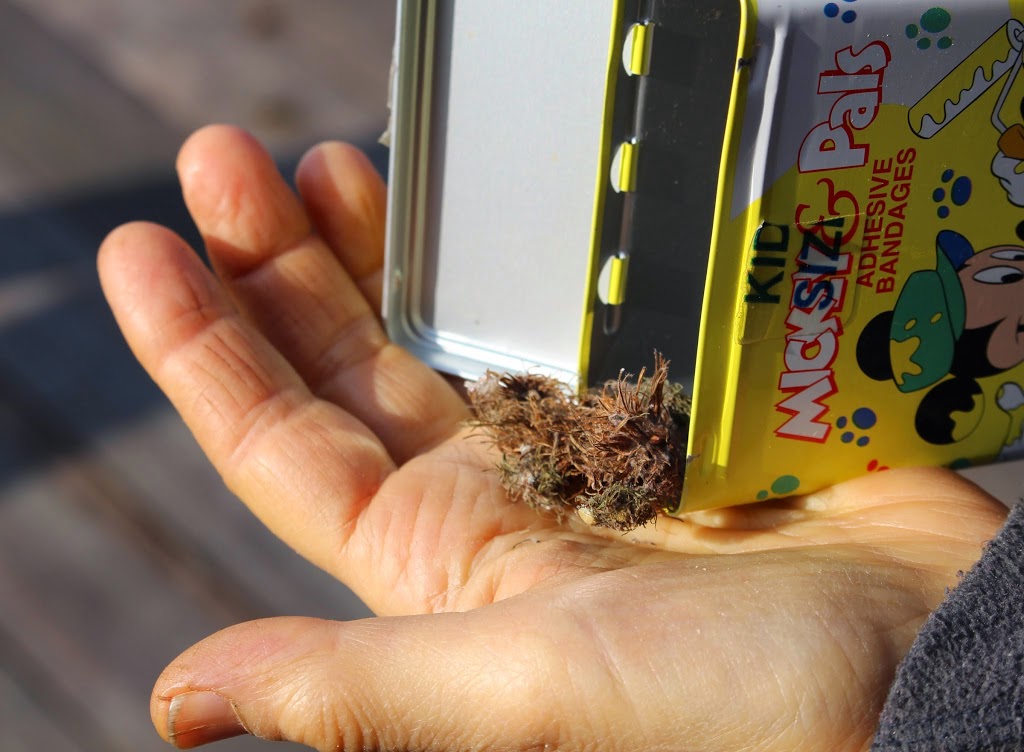
One group of plants in need of this special treatment are my maypops, Passiflora incarnata. Yes, Passiflora genus is that of passionflower, and maypop is a hardy species of passionflower, native to eastern U.S.. It bears the same breathtaking flowers, whose intricate arrangement of flower parts was used by Christian missionaries to teach native Americans about the “passion” of Christ, as the tropical species.  And, like the tropical species, flowers are followed by egg-shaped fruits filled with air and seeds around which clings a delectable gelatinous coating. You know the flavor if you’ve ever tasted Hawaiian punch.
And, like the tropical species, flowers are followed by egg-shaped fruits filled with air and seeds around which clings a delectable gelatinous coating. You know the flavor if you’ve ever tasted Hawaiian punch.
Maypop parts ways with tropical passionflowers, which are woody vines, in being an herbaceous vine. The roots live year ‘round but the above ground portions of the plant die back each winter.
Besides creating a microclimate for the maypops, I also chose to plant them in an existing microclimate to their liking. That is on the south side of my woodshed, where the sun bears down to provide extra warmth in summer. (Another goal was to let the vines each summer cover a trellis that would give the woodshed some shade to prevent the firewood from drying out to much.) These plants of southeastern U.S. like their summers hot.
Soil moderates temperatures so never get as cold in winter as the air — or, in summer, as hot as the air. Five feet down, soils remain at a balmy 50°F year ‘round. Shallower depths are commensurately colder in winter and warmer in summer than deeper down.
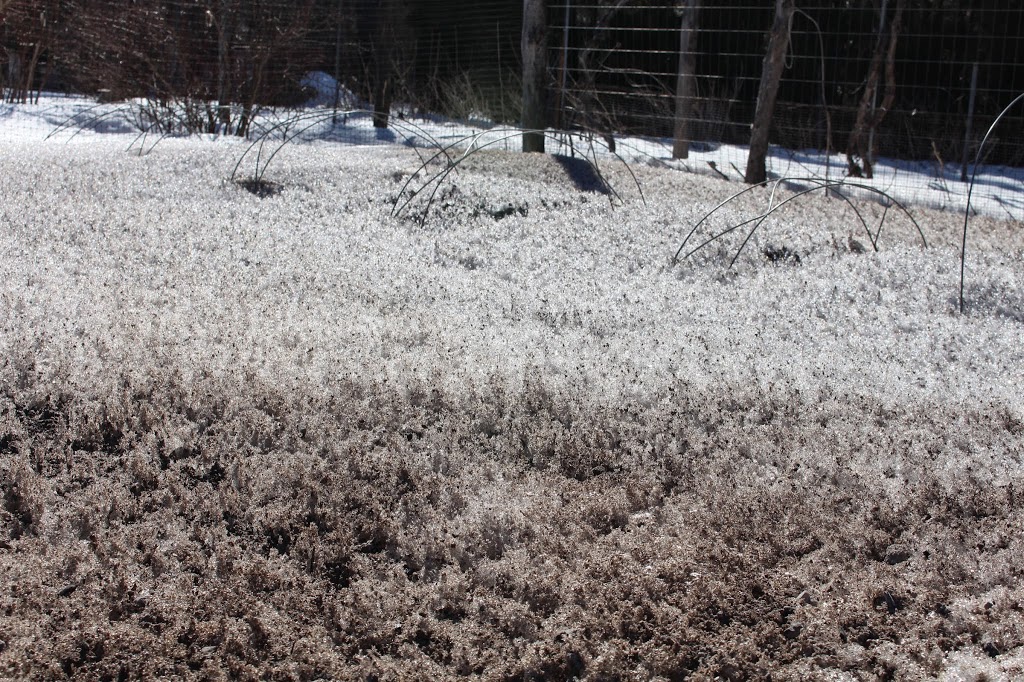
Maypop is borderline hardy this far north. Insulating the ground around the plants will keep temperatures around the roots from dropping too low. Hence the snowy mulch.
As maypop grows through the summer, new flowers and then fruits appear. The longer the growing season, the more fruits the plants bear. Although I want to keep the ground from getting too cold in the depths of winter, I’d like it to warm up quickly in spring to get the plants going.
Wood chips, straw, snow, or any other mulch is going to put the brakes on soil warming, so, ideally, the mulch should be removed after the coldest part of winter is past. Except if that mulch is snow, which will melt.
Ugly but Delicious
Wandering through the snow to the other side of the farmden, I come upon another fruit, this one ready to pick and eat right now! Medlar. (Medlar and maypop each warranted a whole chapter in my book Uncommon Fruits for Every Garden.)
Medlar fruits resemble small, russeted apples (a relative), tinged dull yellow or red, with their calyx ends (across from the stems) flared open.  It’s peak of popularity was in the Middle Ages. And though popular, it was made fun of for it’s appearance; Chaucer called it the “open-arse” fruit.
It’s peak of popularity was in the Middle Ages. And though popular, it was made fun of for it’s appearance; Chaucer called it the “open-arse” fruit.
That old-fashioned look extends to the tree itself, which even this time of year is attractive with the elbowed contortions of its branches. In spring, the blossoms, which resemble wild roses, are borne singly at the ends of branches and, opening late so that each is cradled in already opened whorl of leaves.
But back to the fruit; its got another quirk, besides its appearance. It’s inedible when first harvested. But after the fruit has sat for a couple of weeks or more indoors, a process called bletting, the once-hard, white flesh turns to brown mush.

Medlar, after bletting
Yechhhh! The flavor, though, has a refreshing briskness with winy overtones, like old-fashioned applesauce laced with cinnamon.
Fruits left on the tree also blet, and my trees are loaded with fruits.
Uh oh. Although medlar is generally pest-free, I see that many of the fruits have what looks like some sort of pest damage. Instead of the smooth, brown mush, flesh of damaged fruits is drier, almost powdery. What is it?
(Almost?) Hardy Orange
More snow more recently fell, and with it came bitter cold, which made me fear for the survival of my hardy orange, Citrus trifoliata. This orange is allegedly hardy to zone 5, but still . . .
The plant is only about four feet tall and there was plenty of snow so I just started piling snow on top of it. The ends of some branches remained exposed, which is okay because they can tell me whether the plant is really hardy.
Hardy orange bears flowers and fruits very similar to sweet oranges except that hardy orange fruits are bitter and very seedy. They could be used — in moderation — for flavoring, though. 
 Mostly I grow it for the novelty of an outdoor orange tree, for the sweetly fragrant blossoms, and for the decorative, green, swirling, recurved spiny stems.
Mostly I grow it for the novelty of an outdoor orange tree, for the sweetly fragrant blossoms, and for the decorative, green, swirling, recurved spiny stems.
Come spring, I;’ll know if just how hardy the hardy orange really is. Temperature the night after covering it dropped to minus 18° Fahrenheit.
 Read more
Read more
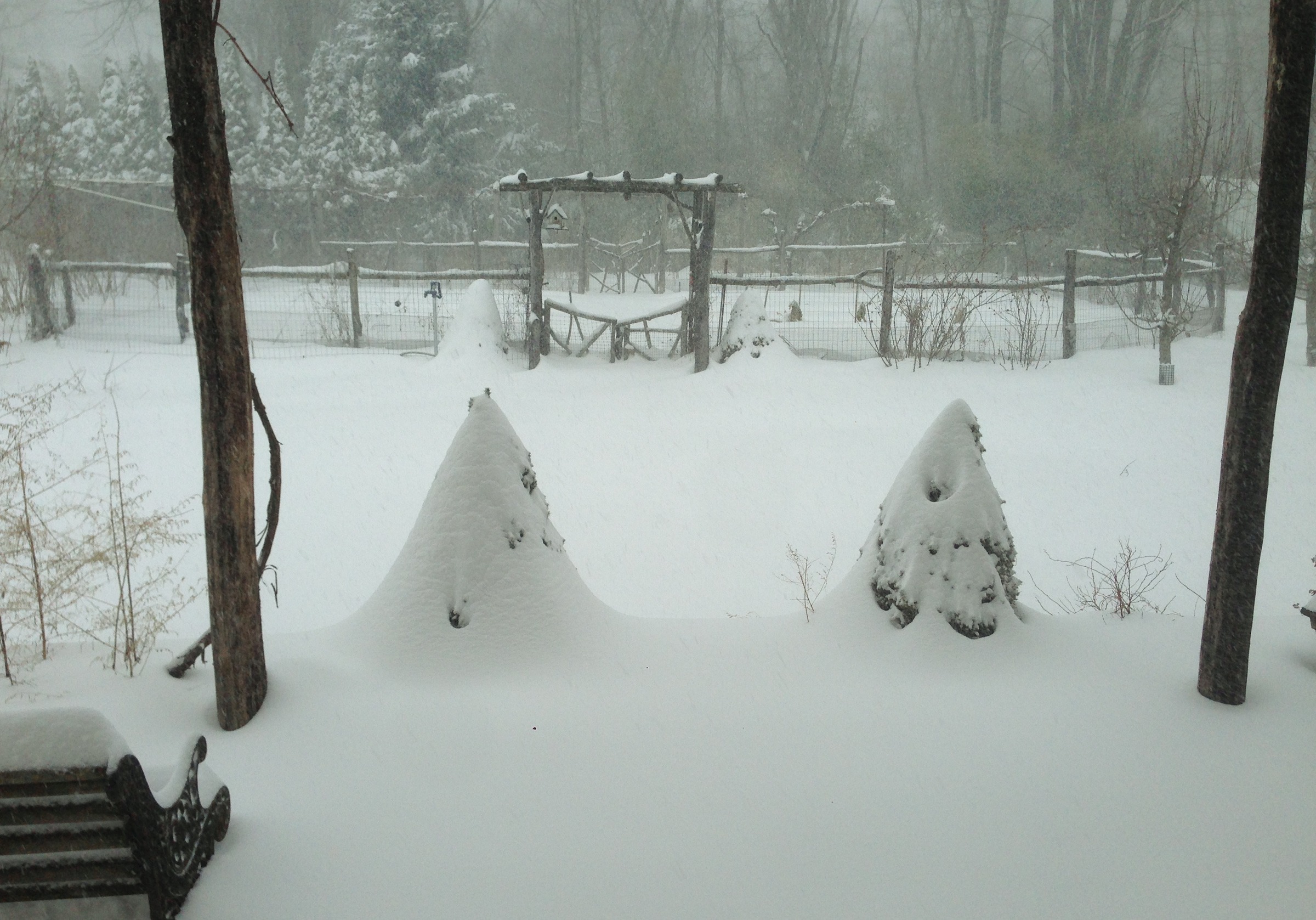








 Both kinds of plants are probably cold-hardy to about zero degrees Fahrenheit, but here winter temperatures, except last winter, typically drop to about minus 20 decrees Fahrenheit. That snowy blanket provides extra protection that the plants might need — especially after last Saturday’s unseasonal low of minus 8 degrees.
Both kinds of plants are probably cold-hardy to about zero degrees Fahrenheit, but here winter temperatures, except last winter, typically drop to about minus 20 decrees Fahrenheit. That snowy blanket provides extra protection that the plants might need — especially after last Saturday’s unseasonal low of minus 8 degrees.









 The flowers don’t exactly jump out at you so you have to get up pretty close to even notice them. Still, they are a sign of plant life in the depths of winter.
The flowers don’t exactly jump out at you so you have to get up pretty close to even notice them. Still, they are a sign of plant life in the depths of winter.
 And, like the tropical species, flowers are followed by egg-shaped fruits filled with air and seeds around which clings a delectable gelatinous coating. You know the flavor if you’ve ever tasted Hawaiian punch.
And, like the tropical species, flowers are followed by egg-shaped fruits filled with air and seeds around which clings a delectable gelatinous coating. You know the flavor if you’ve ever tasted Hawaiian punch. It’s peak of popularity was in the Middle Ages. And though popular, it was made fun of for it’s appearance; Chaucer called it the “open-arse” fruit.
It’s peak of popularity was in the Middle Ages. And though popular, it was made fun of for it’s appearance; Chaucer called it the “open-arse” fruit.

 Mostly I grow it for the novelty of an outdoor orange tree, for the sweetly fragrant blossoms, and for the decorative, green, swirling, recurved spiny stems.
Mostly I grow it for the novelty of an outdoor orange tree, for the sweetly fragrant blossoms, and for the decorative, green, swirling, recurved spiny stems.





