Pruning, Not Too Late
 |
| Kiwi, before pruning |
 |
| Kiwi, after pruning |
 |
| Kiwi, before pruning |
 |
| Kiwi, after pruning |
 |
| Weeping cherries, Bryn Mawr, PA |
 |
| Stewartia monophylla at the Barnes Foundation, PA |
 |
| Stewartia japonica |
 |
| Witchhazel, here at the farmden |
Write in your heirloom favorites soon . . . the giveaway (see below) will end Wednesday, March 27th at 1 pm.
And now for the giveaway: A “High Mowing” cap and their boxed set of seeds for heirloom vegetable lovers. The box includes packets from such old-time favorites as Brandywine tomato, Red Salad Bowl lettuce, Detroit Dark Red Beet, Red Russian Kale, and others. To enter this giveaway, in the “Comments” box below tell us about some of your favorite heirloom vegetables. Winner of both the hat and the box of seeds will be selected randomly and contacted for mailing by email.
Here, then, is my schedule for sowing and planting some vegetables (after June 1, all plantings are outdoors):
 |
| Some white tomatoes, grown years ago |
Two or three people have already asked me, “Are you growing anything special this year?” Each time I had to stop and think: Am I? Then I feel, yes, I should be growing something new each year. Then, on the other hand, I feel, what with the vagaries of the weather and pest problems, that it’s interesting enough just to grow every year what I’ve grown in previous years. Reinforcing that last thought is a quote from Charles Dudley Warner (My Summer in a Garden, 1870): “I have seen gardens which were all experiment, given over to every new thing, and which produced little or nothing to the owners, except the pleasure of expectation.”
 |
| Apricots, in my future — I hope. |
Another “new” plant for this year is honeyberry (Lonicera edulis), sometimes called edible blue honeysuckle. This is another plant I grew many years ago. It performed poorly because of the poor care I gave it which was mostly because of the poor flavor of the one berry I tasted. But honeyberry is a new fruit, in the same place, development-wise, as the apple might have been 2,000 years ago. New varieties have come down the pike and I’m ready to try these newbies.
 |
| Ramps, now sprouting |
 |
| Forget about the nuts; yellowhorn is worth growing even just for its flowers |
 |
| Nanking cherry stems are hidden behind the oodles of fruit this plant bears |
Mar 9: Philadelphia Flower Show: FRUIT GROWING SIMPLIFIED
Mar 10: Philadelphia Orchard Project: LECTURE AND HANDS-ON WORKSHOP ON PRUNING FRUIT TREES, SHRUBS, AND VINES
Mar 16, Thetford, VT: FEARLESS PRUNING
April 6, Maine Garden Day (Lewiston, ME): FRUIT GROWING SIMPLIFIED, MULTI-DIMENSIONAL VEGETABLE GARDENING
April 10, Rosendale (NY) Library: BACKYARD COMPOSTING
April 20, Berkshire Botanical Garden (Stockbridge, MA), GROW FRUIT NATURALLY, BLUEBERRIES: RELIABLE & EASY TO GROW, HEALTHFUL, & DELICIOUS
April 28, WV Master Gardener’s Assoc (Flatwoods, WV): MY WEEDLESS GARDEN
May 11, Margaret Roach’s Garden (Copake Falls, NY): BACKYARD FRUIT LECTURE (morning), GRAFTING WORKSHOP (afternoon)
May 16, Brookside Gardens (Wheaton, MD): MY WEEDLESS GARDEN
June 1, The Cloisters (NYC): MEDIEVAL FRUITS YOUCAN GROW TODAY
————————————
The official start for this year’s growing season, which I count as the day when I sow my first vegetable seeds, will begin momentarily. Actually, the season should have already been underway, as of February 1st, but I put in my seed order a little late so am tapping my foot and (im)patiently waiting for the seeds to arrive in the mail. That first sowing is, of course, indoors, and the seeds will be onions, leeks, and celery. The most interesting of the three, as far as growing, is onion.
 Down in my cold basement I dug last season’s begonia bulbs (actually, they are tubers, or thickened, underground stems) out of storage. I tucked them in among some wood shavings in an old aquarium last autumn. In contrast to the big, fat amaryllis bulbs, the begonia bulbs didn’t look like much more than rough, brown clods of soil. Moved to warmth, with the sawdust kept moistened with a bit of water — too much and the tubers will rot — those lifeless-looking lumps should sprout leaves, and then, by June, flowers. The appeal of the begonias, which I grew from dust-like seeds a couple of years ago, is that the foliage is attractive and the fire-engine red flowers are, in contrast to those of amaryllis, proportional to the size of the leaves and the plant, and they’re borne nonstop right up until autumn.
Down in my cold basement I dug last season’s begonia bulbs (actually, they are tubers, or thickened, underground stems) out of storage. I tucked them in among some wood shavings in an old aquarium last autumn. In contrast to the big, fat amaryllis bulbs, the begonia bulbs didn’t look like much more than rough, brown clods of soil. Moved to warmth, with the sawdust kept moistened with a bit of water — too much and the tubers will rot — those lifeless-looking lumps should sprout leaves, and then, by June, flowers. The appeal of the begonias, which I grew from dust-like seeds a couple of years ago, is that the foliage is attractive and the fire-engine red flowers are, in contrast to those of amaryllis, proportional to the size of the leaves and the plant, and they’re borne nonstop right up until autumn. |
| Impatiens in Puerto Rico rainforest, El Yunque |
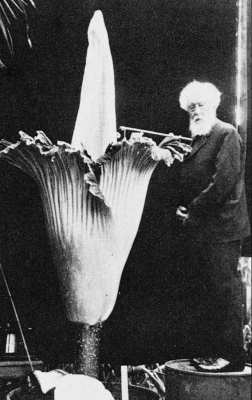 |
| Hugo de Vries and amorphophallus, 1937 |

