LITTLE ITALY IN THE HUDSON VALLEY
Curing my Olive Harvest
My olive harvest, about which I recently wrote, was such a success that I want to up my production beyond this year’s bountiful 6 fruits. Those 6 fruits, once cured, were truly delicious. (Yes, the halo effect — my assessment of them veiled by my having grown them — could come into play.)
Part of the reason for the fruits’ high quality was how I cured them. Not very complicated: I just let them sit and dry out. After about two weeks, they had lost their bitterness, and, without the distraction of salt, oil, or spices, their rich, olive flavor shined through.
New Roots, New Shoots
Part one of my twofold plan to increase production is to put the plant into a larger pot. A larger pot makes for a larger plant; a larger plant has more branches on which to hang more fruit.
Looking more closely at the plant told me that re-potting was necessary immediately! New flower buds are already beginning for the next crop. Because the plant is moving up to a larger pot, no root pruning is necessary. I put some potting soil in the bottom of a pot, set the exposed root ball on top of the soil, loosened some roots along the outside of the root ball, and packed new soil in the space between the root ball the the side of the pot.
With soil firmed and a thorough watering, the roots have a happy home — for a year or two, when root pruning and re-potting become necessary. If moved up to a yet larger pot, the plant would be too unwieldy to muscle indoors and out.
Part two of my plan to increase production is pruning. To prune any fruit plant for best yield and quality, you have to know something about how the particular plant bears its fruits. For instance, peaches are pruned very differently from apples because peaches bear only on one-year-old wood and apples bear on wood a couple of years old on up to a decade or older. One of the goals in pruning peaches is to coax enough new growth this year for a good crop next year.
To figure out how to best prune an olive, I referred back to The Pruning Book (which I wrote, and also details pruning of apples, peaches, and just about every other plant). “Fruits form in leaf axils along, but not to the end of, the previous year’s stems (and sometimes from dormant buds in one- or two-year-old wood).”
So olive fruits something like a peach, on young wood. Actually more like an apricot, which bears fruit on wood from one to three years old.
My ploy was too shorten some stems, focussing on those making the plant look gawky. Without sacrificing yield, shortening stems has the benefit of encouraging new, branching growth. More branching will make the plant look prettier and provide more young stems on which to hang fruit next year.
Sleep, Sweet Fig
Going from the sun-drenched window, in front of which my olive tree basks, all the way down to the basement, I check out another Mediterranean fruit, my potted fig trees. What’s happening with them? Nothing, I hope.
Now is a crucial time of year for a potted fig tree. The goal is to keep them dormant. Unfortunately, just a bit more warmth or a bit more light and they’ll start to awaken. If awakened, new growth will be soft and sappy, even if the plants sit in front of a sunny window. Then, when the plants finally go outdoors, intense sunlight, wind, and cooler temperatures are apt to burn back such growth.
 Temperatures stay relatively consistent and cool (40-45°F.) in my basement and it’s dark down there, so the plants generally stay dormant until sometime, probably next month, when I can set them outside. Keeping the plants slightly on the dry side also helps hold back growth.
Temperatures stay relatively consistent and cool (40-45°F.) in my basement and it’s dark down there, so the plants generally stay dormant until sometime, probably next month, when I can set them outside. Keeping the plants slightly on the dry side also helps hold back growth.
Last year was perfect. I moved the dormant figs outdoors while the weather was still cool without temperatures dropping too low below freezing. (Dormant figs tolerate temperatures down to the low 20s.) Growth began in synch with increasing temperatures, culminating in branches draped with soft, ripe figs by summer’s end. I’m planning for a repeat performance.
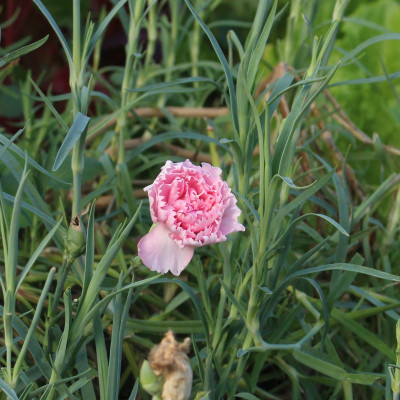

 Carnations are among flowers, along with baby’s-breath, lilies, snapdragons, and most orchids, whose ethylene production ramps up as senescence begins. These flowers also are very sensitive to the effects of ethylene, which speeds aging, which generates more ethylene, which further speeds aging, which . . .
Carnations are among flowers, along with baby’s-breath, lilies, snapdragons, and most orchids, whose ethylene production ramps up as senescence begins. These flowers also are very sensitive to the effects of ethylene, which speeds aging, which generates more ethylene, which further speeds aging, which . . .