Come Visit My Farmden
/7 Comments/in Gardening/by Lee ReichThis Sunday, June 24th, 2018, from 1-4:30 pm my garden/farmden is open to the public as part of the Garden Conservancy’s Open Days program. The Garden Conservancy is an American nonprofit organization founded in 1989 and dedicated to preserving exceptional gardens and landscapes. The $7 admission cost to each Open Day garden helps fund their efforts. For more information about my farmden and other local gardens open that day (and through summer), go to https://www.gardenconservancy.org/open-days/garden-directory/springtown-farmden

My Dog and I Have Odd Tastes
/8 Comments/in Soil, Vegetables/by Lee ReichIn My Opinion . . .
Note: The following editorial comments represent the opinions of the writer and do not necessarily represent the opinions of the publisher.
I don’t understand the current — decades long, now — infatuation with the “stinking rose,” as garlic used to be called. Not to reveal my age, but I don’t remember ever seeing, smelling, or tasting garlic in my youth. Not that I didn’t; I just don’t remember it if I did. At any rate, in my family circle, at least, it would not have generated the undue enthusiasm it does these days. Whole festivals, for instance!
I don’t dislike garlic. Mostly, when I’ve used it, it’s flavor is lost when cooked. Except when roasting turns the texture satiny and the flavor bite-less; then it’s quite delicious spread on bread or baked potato, or mixed with vegetables. Mmmmm.
But still not worth planting. It’s my belief that many gardeners devote all too much space to growing garlic. Is home-grown garlic really that tasty, tastier than what you can pick off a supermarket shelf or from a bin at the farmers’ market?
I’ve seen very small vegetable gardens in which a third of the area was devoted to the stinking rose. For my money, I’d rather be picking fresh lettuce, asparagus, or peas — all of which taste significantly different and better within minutes of harvest than when bought from any market, farm or otherwise. Or peppers, tomatoes, sweet corn, or green beans, because I can choose the best tasting (to me) varieties to plant in my garden.
As you might guess, I don’t grow garlic — not in my vegetable garden, at least. Why devote even a square foot of space in that compost-rich, drip irrigated, sun-drenched ground to such a thankless vegetable?
I do sometimes grow garlic in various patches of open ground in the large patch of gooseberries, grapes, and a miscellany of other plants behind my garden. The only improvement that soil experiences is annual mulching with autumn leaves, which has enriched the ground below with humus. But no irrigation, which the garlic, planted in early autumn and then harvested the following summer, hardly needs because it can run on rainfall that falls in autumn through spring.
Garlic doesn’t seem to get the hint that I don’t particularly want to grow it. Enough bulbils that form at the tops of scapes touch down each year to make new garlic plants. Most are spindly, giving rise to Lilliputian cloves.  But if I want some garlic flavor in spring, I can pull stalks out of the ground, peel off the outer covered of leaf sheath, and chop up the ivory white lower portion for use. Many I just pull out and toss into the compost pile; the garlic is getting weedy.
But if I want some garlic flavor in spring, I can pull stalks out of the ground, peel off the outer covered of leaf sheath, and chop up the ivory white lower portion for use. Many I just pull out and toss into the compost pile; the garlic is getting weedy.
Okay, you garlic lovers, go ahead and pelt me with tomatoes. But hold the garlic.
Sammy Stalking
My dog Sammy has grown very fond of stalks. Asparagus stalks. Why can’t he channel that stalky affection to the garlic sprouting behind my garden? Perhaps some culinary magic with garlic poured over his dog food and guided walks over to some of the growing clumps could bring him around.
I planted asparagus outside the fenced vegetable garden with the knowledge (ha!) that no furry animals would dine on it. Sammy has plowed his way through or gracefully leapt over the temporary chickenwire enclosure meant to keep him asparagus-free. A recently purchased electric fence should keep him at bay — also from the persimmons, another of his favorites, later in summer. 
Of Mulch Importance
On a more serious note, now, with recent rains maintaining good soil moisture, is an ideal time to mulch. Earlier this season, mulch would also have been good, except that it would have delayed soil warming and, hence, seed germination, planting and growth of annual vegetables and flowers.
Mulch spread atop dry soil has to be wetted before letting water percolate down into the ground below.  If spreading mulch is delayed until the soil turns dry, all the more water will be required to give the soil below a good drenching.
If spreading mulch is delayed until the soil turns dry, all the more water will be required to give the soil below a good drenching.
A large pile of wood chips sits on the far side of my wood pile, compliments of local arborists. Day by day, I’m spreading it for an attractive, soil enriching, moisture sealing blanket over my soil — even around my volunteer garlic plants.
“Worms” Good and Bad
/2 Comments/in Pests/by Lee ReichNematodes Galore
The name ”nematode” doesn’t conjure up a creature that you’d normally want to make friends with. It’s other name, roundworm, seems even more repulsive and is, in fact, also a name applied more specifically to a nematode that infects humans and dogs.
Like it or not, nematodes are all around us, with over 25,000 species described so far that inhabit diverse ecosystems from thousands of feet deep in the Earth to mountain tops, and from deserts to rain forests. Many are visible only under a microscope; some are two inches long. A square yard of soil can be home to more than a million nematodes, and we humans can be host to about 35 species.
Do we want our plants to cozy up with them?
A number of nematodes infect plants, resulting in stunted growth and, often, swellings on roots or stems.
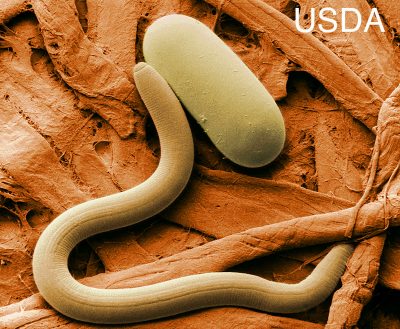
Soybean cyst nematode
Their common names — root knot nematode, stubby root nematode, cyst nematode, lesion nematode — describe some of the symptoms. These plant pathogenic nematodes can do further ill by transmitting bacterial or viral diseases to plants.
I’m not particularly worried about nematodes in my garden. For one thing, they’re more prevalent in warmer climates. Also, good gardening practices, such as enriching the ground with compost, leafy mulches, and other organic materials, and crop rotation go a long way to thwarting such problems.
If I did have a nematode problem, or suspected one, I could reach into a quiver of “organic” solutions. Marigolds can suppress nematodes. Not just a plant here and there, though, but a solid planting of giant, African marigolds. Mustard has a similar effect, whether grown, like the marigolds, as a cover crop, or applied as a seed meal, which also happens to be a slow-release nitrogen fertilizer.
Chitosan, made from the shells of crustaceans and the active ingredient found in commercial products such as Serenade, reputedly bolsters plant defenses against nematodes and other pathogens. (My casual experimenting with Serenade against apple diseases found no benefit.)
Welcome “Worms”
In the same way that just about no one with an eye patch is a pirate, very few “nematodes” are bad guys. In the garden, so-called “predatory” nematodes are better than neutral; they are the “good guys,” preying on a wide range of garden pests.
Some of the most common beneficial nematodes are Steinernema carpocapsae, S. feltiae, and Heterorhabditisheliothidis bacteriophora. These three nematodes vary in their habits although they all attack a wide variety of garden pests. Steinernema carpocapsae is an “ambusher forager” that lies in wait near the soil surface for unwary pests to wander past. Heterorhabditisheliothidis bacteriophora is a “cruise forager” that moves around through various depths of soil, ready to pounce upon unsuspecting sedentary pests. The habitat and hunting behavior of S. feltiae nematodes is intermediate to the other two.

Waxworm releasing beneficial nematodes
Beneficial nematodes can be purchased. To be effective, they must be shipped at the right growth stage and applied without their drying out. Even then, annual applications are frequently needed.
Some strains of the beneficial nematodes can survive and multiply in the soil year after year. I imagine that my garden soil has plenty of “good” nematodes; perhaps more would be better. Some day I may extract some of the “good guy” nematodes from my soil, multiply them, and then re-apply them to my ground.
For now, I intend to get hold of a starter supply of native, perennial nematodes and multiply my holdings, a process which I think will have the added benefit of being fun and interesting. The three kinds of nematodes extracted from soils in central New York, are available for purchase from http://blogs.cornell.edu/ccefieldcropnews/2018/02/28/discount-available-on-biocontrol-nematodes-to-protect-alfalfa-corn-crops/.
With nematodes in hand, a nematode host is needed if I’m going to multiply them. Waxworms, sold for fishing bait, are a convenient host. The waxworms get incubated with the nematodes which, after a couple of weeks, are rinsed free of the waxworms with water.
The aqueous suspension of nematodes is then ready for application. To prevent their drying out, they’re best applied in early morning or evening along with plenty of water. If all goes as planned, they should establish and multiply to kill such pests as wireworms that bore into carrot and radish roots, plum curculio that attack apple, plum and peach fruits, and any cutworms that attack just about everything.
Come Visit My Farmden
Last minute notice: Come visit my farmden, in real life, on June 24th. As part of the Garden Conservancy Open Days program, I’ll be hosting visitors between 1 pm and 4:30 pm on that day. For more information about my farmden and other local sites, go to the https://www.gardenconservancy.org/open-days/open-days-schedule/ulster-county-ny-open-day-2.

