SOMETIMES CALLED SPARROW GRASS, SOMETIMES ASPARAGOS
/20 Comments/in Vegetables/by Lee ReichMany Reasons to Grow Asparagus
In my book Weedless Gardening, I begin the section about asparagus with the statement “Forget about the usual directives to excavate deep trenches when planting one- or two-year-old crowns of asparagus.” More about planting in a bit; let me first lay out my case about why YOU should grow asparagus.
With most vegetables, by the time you taste them fresh-picked somewhere, it’s too late in the season to plant them in your garden. Not so with asparagus.  Borrow a taste from a neighbor’s asparagus bed, or from a wild clump along a fencerow, and you’re likely to want some growing outside your own back door. Minutes-old asparagus has a very different flavor and texture (both much better) than any asparagus that reaches the markets. The time to plant is now.
Borrow a taste from a neighbor’s asparagus bed, or from a wild clump along a fencerow, and you’re likely to want some growing outside your own back door. Minutes-old asparagus has a very different flavor and texture (both much better) than any asparagus that reaches the markets. The time to plant is now.
A big plus for asparagus is that it’s a perennial plant, so once a bed is planted, more time is spent picking than any other activity. An established planting can reward the gardener with tender green spears for a half a century or more. My asparagus bed is thirty-six years old and about twenty-five feet long; on every warm day, the bed offers enough stalks for a meal for two.
Deer and rabbits don’t have a taste for asparagus so no need to plant it within the vegetable garden or any protected area. (My dogs have eclectic palates, and they joined in on the harvest until I made clear that asparagus was not dog food.) Planting asparagus beyond the confines of the vegetable garden works out well because the lacy, green foliage stands as a backdrop for perennial flowers. Or, it can soften the line of a wall or fence.
Planting asparagus beyond the confines of the vegetable garden works out well because the lacy, green foliage stands as a backdrop for perennial flowers. Or, it can soften the line of a wall or fence.
Traditional Planting Method is Unduly Hard
Now, back to what I wrote about planting asparagus in Weedless Gardening, (available, by the way, at the usual sources as well as, signed, from my website, here).
The traditional method for planting an asparagus bed entails digging a trench a foot or more deep, setting the roots — one-year-old roots establish best — in the bottom with a covering of a shovelful of soil, then filling in the trench gradually as the stalks grew.
Whew! I planted my own asparagus bed just deep enough to cover the upward pointing buds from which the roots radiate, and the plants do just fine.
The main reasons for the traditional deep planting were to protect the crowns from overzealous hoes or other tillage implements, and from knives during harvest. But I don’t till my asparagus bed. I just pile on some mulch every year. And I harvest by snapping the stalks off with my fingers, rather than cutting into the soil with a knife.
Gardeners with patience sow seeds, which need a year more in the ground than roots before harvest can begin. Seed sowing is straightforward, except that germination is slow. Soak the seeds in water for a few hours before sowing to shorten germination time.
Whether starting with seeds or plants, the bed needs to be planted in full sun, with eighteen inches between plants in the row, and four feet between rows.
Tune into Asparagus’s Life Cycle
Although asparagus roots live on year after year, the feathery tops turn brown and die back to the ground every fall.  Then, when the spring sun warms the soil, energy stored in the roots fuels growth of the spears. As the spears grow higher and higher, feathery green branches unfold. Photosynthesis within these green branches pumps energy to the root system, energy that keeps the roots alive through the winter and fuels early growth of spears the following spring, thus completing the plant’s annual cycle. (The true leaves of asparagus, which are the small scales on the stems, are much reduced in size and function; the green stems take on most of the job of photosynthesis for this plant.)
Then, when the spring sun warms the soil, energy stored in the roots fuels growth of the spears. As the spears grow higher and higher, feathery green branches unfold. Photosynthesis within these green branches pumps energy to the root system, energy that keeps the roots alive through the winter and fuels early growth of spears the following spring, thus completing the plant’s annual cycle. (The true leaves of asparagus, which are the small scales on the stems, are much reduced in size and function; the green stems take on most of the job of photosynthesis for this plant.)
Harvesting asparagus steals some of the energy that had been stored in the roots. The plant must build adequate reserves before tender stalks can be spared for our plates, and then each season left enough time to grow freely to replenish its energy reserves.
The first season of planting, no asparagus is harvested; if good growth was made the first season, some can be harvested the second season. The plants are ready for a full harvest by the third season.
Full harvest means cutting all stalks from the time they first emerge until about the end of June.  Remember, the plants do need some time to nourish their roots in preparation for winter. Following the last harvest, all new green stems are left untouched until their summer job is over, as they turn brown in the fall.
Remember, the plants do need some time to nourish their roots in preparation for winter. Following the last harvest, all new green stems are left untouched until their summer job is over, as they turn brown in the fall.
Asparagus grew wild along the shores of the Mediterranean before plants were transplanted to Greek and Roman gardens. The steaming dish of asparagus on my table today is virtually identical to the asparagus enjoyed by the ancients over 2000 years ago. Even our word for the vegetable is nearly identical to, and derived from, the Greek word asparagos.
Asparagus came to America with the early colonists and has been cultivated extensively here since then. The red berries borne on female plants attract birds that spread the seed, so asparagus now pops up as an “escape” from cultivation along fencerows and roadsides.
PLANT STRAWBERRY PLANT(S)
/6 Comments/in Fruit/by Lee ReichHumble Appearing Beginnings
The UPS man’s face is a familiar one this time of year, as he brings me boxes and bags of plants from all around the country. I can’t count how many times I’ve met his brisk walk up the driveway to retrieve a box of strawberry plants. A strawberry bed languishes after a few years, typically five years, and when that happens, I just choose a new site and order new plants.

Epsey strawberry, painted in 1911
I begin again with new plants, because although strawberries are perennial plants, old plantings eventually pick up diseases from wild strawberries and related plants. By planting a new bed the year before the old one is due to expire, there’s no break in enjoying fresh strawberries every June.
Opening the box of strawberry plants just arrived provides a sorry sight to the eyes: twenty-five plants, leafless or nearly leafless, bound with a rubber band into a package small enough to hold in my fist. But I take heart; the plants are dormant and, given warmth and soil, will come to life. Immediately as I say good-bye to the UPS guy I open the plastic bag to make sure there’s some moisture within. If not, I add some and reseal the bag. In either case I put the bag in the refrigerator until I’m ready to plant.
Planting Location and Design
Let’s hold off planting a minute and see what type of site I choose for my strawberry beds. The plants thrive best with full sun (at least 6 hours per day with Ol’ Sol beaming directly on the plants) and in a soil that is both well-drained and rich in organic matter. Anything less than the above and fruit flavor suffers and plants are more prone to disease.
Strawberry plants spread by runners, which are stems that creep along the ground forming new plants at intervals along their length. 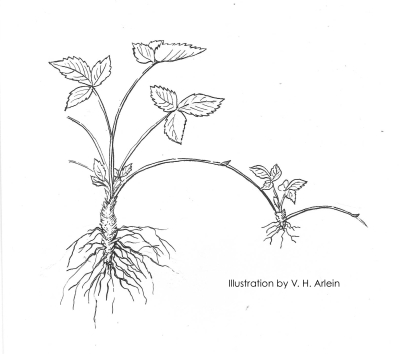 Eventually, plants in a strawberry bed should be 6 to 12 inches apart. The “matted row” system of strawberry planting makes full use of these runners. Plants are set far apart (4 feet between rows and 2 feet between plants) and the spaces between the plants fill in with runner plants which fruit the following season.
Eventually, plants in a strawberry bed should be 6 to 12 inches apart. The “matted row” system of strawberry planting makes full use of these runners. Plants are set far apart (4 feet between rows and 2 feet between plants) and the spaces between the plants fill in with runner plants which fruit the following season. 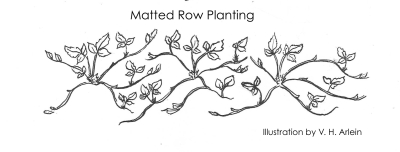 The matted row is allowed to fill in to a width of 2 feet, and all plants attempting to spread beyond that width are kept in bounds with a rototiller or by hand. With age, that 2 foot ribbon rapidly becomes overcrowded unless old plants are weeded out.
The matted row is allowed to fill in to a width of 2 feet, and all plants attempting to spread beyond that width are kept in bounds with a rototiller or by hand. With age, that 2 foot ribbon rapidly becomes overcrowded unless old plants are weeded out.
I prefer the opposite extreme in strawberry planting systems, the “hill” system, whereby plants are set in a double row with 12 inches between the rows and between plants in the row. (If there’s more than one double row, the next double row is 3 feet away.) 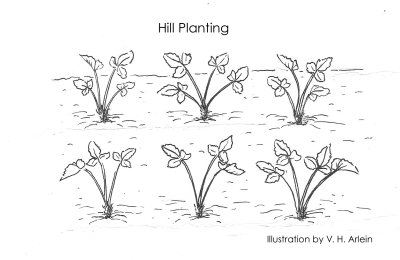 The hill system demands the somewhat tedious job of pinching off all runners through the summer, but the planting stays neater and yields the most berries the first bearing season.
The hill system demands the somewhat tedious job of pinching off all runners through the summer, but the planting stays neater and yields the most berries the first bearing season.
The “spaced plant” system splits the difference between the hill system and the matted row system. Plants are set moderately far apart, and only 4 or 5 daughter plants are allowed to take root, carefully spaced around each mother plant.
And Into the Ground They Go
Actual planting of strawberries in the ground takes little time if the soil is in good condition — weed-free, rich in humus, and not too dry and not too moist. Gently squeeze a handful; it should crumble.
I prepare the plants by retrieving them from the refrigerator, undoing the bundle, and trimming the roots back to three or four inches. Then I drop the plants into a shallow pan of water to keep them moist while I plant.
To plant, I thrust a trowel straight down into the soil, then pull the handle towards me enough to open up a slit for a plant.  With the roots fanned out by my other hand, the trimmed plant’s roots fit easily into the waiting slit. Planting is completed as I remove the trowel and firm soil against the roots with the heel of my hand.
With the roots fanned out by my other hand, the trimmed plant’s roots fit easily into the waiting slit. Planting is completed as I remove the trowel and firm soil against the roots with the heel of my hand.
Planting depth is important. Set too shallow and the plants dry out, set too deeply and they suffocate. The ground line should go right through the middle of the crown, which is actually a stem that’s been telescoped down so that each leaf grows off it right next to the next leaf along the stem, rather than a few inches apart, as in most stems.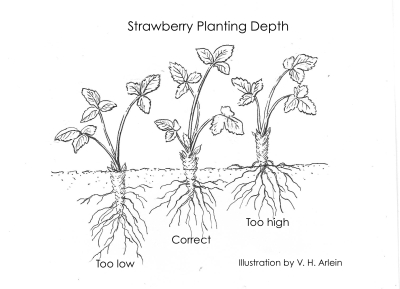
A number of years back I was helping my friend Helene plant her first strawberry bed. Sorry Helene, gotta write about it. My job was to open up the holes; your job was to plant. After a dozen holes, I glanced back over my shoulder to check your progress. You had listened carefully: each plant was set with the ground line through the middle of the crown, against which the soil was firmed, even lovingly smoothed. And, as I had instructed, you had neatly fanned out each plant’s roots. How did I know? Because the plants were upside down, with their roots splayed upward in the air!

First blueberries on heels of last strawberries
TEASING APART HYDRANGEAS
/3 Comments/in Flowers, Pruning/by Lee ReichGood Answer
When someone asks me how they should prune their hydrangea, I give them the answer that most people don’t like to any question “It depends.” What else can I say? It DOES depend. One or more of a few species of hydrangeas commonly make their home in our yards, and you have to approach each, pruning shears or loppers in hand, differently.
Let me tease apart the answer by, first, taking a look a what hydrangea or hydrangeas we may be growing, and then how they grow and flower, which, in turn, speaks to when and where to start snipping away.
Mopheads and Lacecaps, and Oakleafs
If the hydrangea plant in question is a shrub bearing blue or pink flowers, it’s a so-called Bigleaf Hydrangea (Hydrangea macrophylla). Mopheads types, also called hortensias, bear softball to volleyball size clusters of florets. Lacecap types bear flat-topped cluster of small, hardly conspicuous florets surrounded by rims of showy, larger, 4-petalled florets.
Whether mophead or lacecap, Bigleaf Hydrangeas flowers open from buds they set up the previous year. Those buds are big and fat, in contrast to the skinny buds that grow out to become shoots.
Prune Bigleaf Hydrangea stems as far as the fat buds while the plants are leafless (now, for instance). Right after bloom, cut the stems further back to near ground level.
Problem is that while the plants can stand up to bitter cold, the flower buds can’t, expiring at temperatures below about minus 5° Fahrenheit. Some varieties set their flower buds lower on the stem than do others. Their buds might more reliably stand up to winter cold if plants are mulched in late fall with some loose organic material like straw or arborists’ wood chips.
Pushing Bigleaf Hydrangea growing further north are some recently developed varieties that bloom on new, growing shoots. These new varieties — the first one of which was named Endless Summer — will bloom anywhere. Blossoms on new shoots unfurl later in the season than those on older wood, too late in some gardens (like mine, some years). Cutting back older shoots after they flower fuels a better show from the young, growing shoots.
Oakleaf Hydrangea (H. quercifolia) is another hydrangea that is very cold hardy, except for it flower buds. Flowers sit on the ends of stems in elongated clusters, like cotton candy. Oakleaf Hydrangea can be pruned just like Bigleaf Hydrangea, except that it grows as a large shrub so need not be cut back so much.
Lack of a flowery show from Oakleaf Hydrangea is no loss because a billowing mound or mounds of the oak-like leaves are attractive in their own right through summer, and also in fall, when the leaves turn rich, burgundy red. Even where winter cold would test the reliability of flowering, Oak Leaf Hydrangea is often planted solely for its form and its leaves.
A Beautiful Climber
Years ago, I planted a Climbing Hydrangea (H. animal petiolaris) at the base of the north wall of my home. It took a couple of years or more to get in gear, but now completely clothes that wall. Though leafless through winter, the peeling, light mahogany bark stands prettily against the brick red backdrop.  Soon the stems will be draped in glossy, green leaves and, a little after that, white flowers that stand proud of the wall on short stalks and glow against their dark backdrop like a starry night.
Soon the stems will be draped in glossy, green leaves and, a little after that, white flowers that stand proud of the wall on short stalks and glow against their dark backdrop like a starry night.
This time of year my pruning consists of shortening shorten flower stalks that reach too far out from the wall and vigorous stems that keep trying to sneak around the wall to clothe the rest of the house. Twice in summer I prune stems again to restrain the plant to only the north wall.
Perhaps I’ll plant another Climbing Hydrangea at the base of my 90 foot tall Norway spruce that with age is thinning out. The hydrangea tolerates sun or shade, and can climb a tree without causing harm.
And, Easiest of All
Rounding out this romp through pruning hydrangeas are two of the easiest to prune plants of the species. The first, Smooth Hydrangea (H. arborescens), grows long shoots from ground level, each capped in early summer with half-foot-wide clusters of of white or pastel flowers. To prune, just lop all stems right to the ground in late winter or early spring.
And finally, we come to PeeGee, sometimes called Panicle, Hydrangea (H. paniculata grandiflora), growing like a small tree or large shrub. This one blossoms in late summer on new growth, so if it is going to be pruned, that needs to be done before growth begins.  With that said, Panicle Hydrangea develops a permanent trunk or trunks, making it difficult to reach high into its dense head for pruning. No matter, because the plant flowers quite well with little or no pruning.
With that said, Panicle Hydrangea develops a permanent trunk or trunks, making it difficult to reach high into its dense head for pruning. No matter, because the plant flowers quite well with little or no pruning.
Hydrangea is only one group of closely related plants where species differ in how they are pruned. Roses would be another example; climbing roses are pruned very differently from rambling roses, which are pruned very differently from . . . you get the picture. Clematis also. For more details about the individual pruning needs of these as well as lots of other trees, shrubs, vines, flowers, fruits, and houseplants, and special pruning techniques like pollarding, mowing and scything (yes, that’s pruning!), and espalier, take a look at my book The Pruning Book. It’s available through the usual sources or, signed, directly from me here.

