INTO THE WOODS
/19 Comments/in Gardening, Planning/by Lee ReichForest Garden Skeptic
“Forest gardening” or “agroforestry” has increasing appeal, and I can see why. You have a forest in which you plant a number of fruit and nut trees and bushes, and perennial vegetables, and then, with little further effort, harvest your bounty year after year. No annual raising of vegetable seedlings. Little weeding, No pests. Harmony with nature. (No need for an estate-size forest; Robert Hart, one of the fathers of forest gardening, forest gardened about 0.1 acre or 5000 square feet.)

Is this a forest garden?
Do I sound a bit skeptical? Yes, a bit. Except in tropical climates, forest gardening would provide only a nibble here and there, not a significant contribution to the diet in terms of vitamins and bulk. A major limitation in temperate climates is that most fruit and nut trees require abundant sunlight to remain healthy; the same goes for most vegetables.
The palette of perennial vegetables in temperate climates is very limited, especially if you narrow the field down to those tolerating shade. I’m also not so sure that weeding would be minimal; very invasive Japanese stilt grass has been spreading a verdant carpet on many a forest floor whether or not dappled by sunlight.
The case could be made — has been made — that some of the dietary vegetable component could be grown on trees. Robert Hart wrote of salads using linden tree leaves instead of annuals such as lettuce and arugula. I’ll admit that I’ve never chewed on a linden leaf. (I’ll give it a try as soon as I come upon one that has leafed out.) My guess is that its taste and texture would leave much to desire.
And how about squirrels? I grow nuts, and part of my controlling them involves maintaining meadow conditions around the trees. This exposes them to predators, including me and my dogs, without their having tree tops to retreat to and travel within. Unprotected, I’ve had nut plants stripped clean by squirrels.
The book Edible Forest Gardens by Dave Jacke offers a very thorough exploration of forest gardening.
But Did I Plant a Forest Garden?
I’ve actually planted a forest garden! Well, perhaps not a forest garden. Over 20 years ago, I did plant a mini-forest. My forest, only about 300 square feet, was originally planted for fun (I like to plant trees), for aesthetics, and for some nutrition. So far I’ve reaped immense visual rewards for my effort.
Here’s what I planted: Bordering a swale that is rushing with water during spring melt and periods of heavy rain went four river birch (Betula nigra) trees. They evidently enjoy the location for they’re now each multiple trunked with attractively brown, peeling bark and towering to about 60 feet in height.

River birch
I also planted 3 sugar maple trees to provide sap for maple syrup for the future. The future is now (except I no longer use enough maple syrup to justify tapping them.) I also planted a white oak (Quercus alba), whose sturdy limbs, I figured, would slowly spread wide with grandeur in about 150 years, after the maples and birches were perhaps long gone. Unfortunately, the white oak died, probably due to winter cold; its provenance was a warmer winter climate. My mistake.
I also planted a white oak (Quercus alba), whose sturdy limbs, I figured, would slowly spread wide with grandeur in about 150 years, after the maples and birches were perhaps long gone. Unfortunately, the white oak died, probably due to winter cold; its provenance was a warmer winter climate. My mistake.
Since that initial planting, I’ve also planted a named variety of buartnut (Juglans x bixbyi), which is a hybrid of Japanese heartnut and our native butternut.

Buartnut (not mine, yet)
I hadn’t realized it, but that tree has grown very fast and now spreads its limbs wide in much that habit as a white oak. The other two trees that I planted are named varieties of shellback hickory (Carya laciniosa). These trees are slow growing but eventually will offer good tasting nuts. They’re quite pretty, even now, with their fat buds.
A Vegetable Also
What about vegetables in my mini-forest? They were not part of my original plan. It turns out that ramps, a delicious onion relative, a native, which I’ve been growing for a few years beneath some pawpaw trees, are spring ephemerals. Spring ephemerals are perennial plants that emerge quickly in spring to soak up sunlight before its blocked by leaves on trees, then grow and reproduce before the tops die back to the ground.
Ramps (Allium tricoccum) are perfect forest vegetable, so I wanted to make the ground beneath my mini forest more forest-y before moving the ramps from beneath the pawpaws. Nothing fancy. All I did was to haul in enough leaves to blanket the ground in the planting area a few inches deep. That leafy mulch will suppress competition from weeds and add organic matter to the soil.

Collecting ramps for transplanting
In just a few years, the ramps will be sufficiently established to provide good eating, perhaps along with some buartnuts and hickory nuts, all from my forest(?) garden.
Drip Opportunity
I’m looking for a site within 20-30 minutes of New Paltz, NY in which to hold a drip irrigation workshop. What I need is a vegetable garden in beds (not necessarily raised beds) for which I would design a drip system. Workshop attendees I would install the system after learning about drip irrigation. Host pays fo materials. Contact me if interested.
ALL ABOUT ONIONS
/10 Comments/in Vegetables/by Lee ReichAn Ode
Onions, how do I plant thee? Let me count the ways. I plant thee just once for years of harvests if thou are the perennial potato or Egyptian onion. If thou are the pungent, but long-keeping, American-type onion, I sow thy seeds in the garden in the spring. And if I were to choose like most gardeners, I would plant thee in spring as those small bulbs called onion “sets.” (Apologies to E.B. Browning)
New Old Ways with Onions
Early March brings us to yet another way of growing onions: sowing the seeds indoors in midwinter. This was the “New Onion Culture” of a hundred and fifty years ago, and, according to a writer of the day, “by it the American grower is enabled to produce bulbs in every way the equal of those large sweet onions which are imported from Spain and other foreign countries.” This is the way to grow the so-called European-type onions.
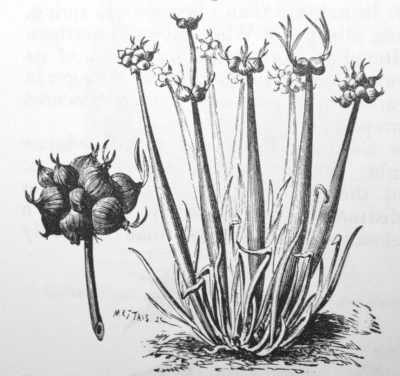
Walking onions
What’s wrong with growing perennial onions, American-type onions, and onion sets? Neither perennial nor American-type onions have the sweet flavor of the famous Vidalia onion, a European type. And onions for sets are generally limited only to the two varieties marketed, Stuttgart and Ebenezer, whose important quality is that they make good sets. A few seeds companies sell sets of a better variety, Forum. In addition to variety, quality of sets is important: too large and they become useless as they send up seedstalks.
The New Onion Culture is a way to grow the large, sweet, mild European onions, such as Sweet Spanish.
The “Method” is as follows: About 10 weeks before the last hard freeze, fill a seed flat with potting soil and use a plant marker to make furrows 1/2-inch deep and one inch apart. Drop about seven seeds per inch into the furrows and then cover the seeds with soil. Fresh seed, less than a year old is best. Water the flat, then keep it moist and warm and covered with of pane of glass. The onions should sprout in a week or two.
Once the onions sprout, remove the plastic or glass and give the seedlings plenty of light. Put the flat either within a few inches of fluorescent lights, on a very sunny windowsill, or in a greenhouse. Each time the seedlings grow to six inches height, clip them back to four inches. The trimmings, incidentally, are very tasty. This indoor stage of plant growing can be bypassed by purchasing onion transplants (not sets), which are sold mail-order in bundles of twenty-five.
Get ready for transplanting a few weeks before the predicted last freeze date. Choose a garden spot where the soil is weed-free, well-drained, and bathed in sunlight. Onions demand high fertility; my plants go into a bed that was dressed with an inch depth of compost last fall. Give the onion seedlings their final haircut, tease their roots apart, then set them in a furrow, or individual holes dibbled with a 3/4-inch dowel. Plant seedlings two to four inches apart, two inches if you want small bulbs, four inches if you want big bulbs.

This may sound like a lot of trouble to grow onions. But for me, midwinter onion sowing inaugurates the new gardening season. The onion is an apt inaugural candidate; it responds to “high culture” starting with careful sowing in fertile soil and moving on to good weed control, timely watering, and, after harvest, correct curing after harvest.
Besides providing this midwinter ritual, onions raised according to the New Onion Culture do have superb flavor.
(The above was adapted from my book A Northeast Gardener’s Year.)
And Still Newer Ways
And now for the “Newer Onion Culture”: American-type onions have the advantage of being better for long-term storage, and newer varieties also have very good flavor. My current favorites are Copra, Patterson, and New York Early. They also are “long day” onions, setting bulbs when the sun shines for 15 to 16 hours daily. “Short day” varieties, which are adapted to the South, would bulb up too soon around here, producing puny bulbs.
There’s more to the “Newer Onion Culture.” A couple of years ago, a local farmer, Jay, of Four Winds Farm, told me he gets good results by just planting seeds in furrows right out in the field.
And even more. Instead of planting 7 seeds per inch indoors in furrows in early March, sow them in flats of plastic “cells” with 4 seeds per cell (each cell is about an inch square).  When transplanting out in the garden, plant each cell with its seedlings intact, spacing them further apart than you would with individual transplants so their roots get adequate water and nutrition. As vegetable growing maven Eliot Coleman wrote in Four-Season Harvest, “the onions growing together push each other aside gently.”
When transplanting out in the garden, plant each cell with its seedlings intact, spacing them further apart than you would with individual transplants so their roots get adequate water and nutrition. As vegetable growing maven Eliot Coleman wrote in Four-Season Harvest, “the onions growing together push each other aside gently.”
Back to my original query: “Onions, how do I plant thee.” Many ways. I’ll do four out of the six ways this season.

Pruning, Flowers
/14 Comments/in Flowers, Fruit, Pruning/by Lee ReichMuch of Pruning is About Renewal
Why am I spending so much time pruning these days? To keep plants manageable and healthy, of course. But also so that flowering and fruiting trees, shrubs, and vines keep on flowering and fruiting. “Renewal pruning” is what does this.

Pruning apple spur
As plant stems age, they — like all living things — become decrepit, no longer able to perform well. But any plant’s show or productivity can be kept up if stems that are too old are periodically lopped back, which promotes growth of new, young, fecund stems. That’s all there is to renewal pruning.
Ah, but the devil is in the details. One important detail is how old is “too old.” That depends on the flowering and fruiting habit of the plant.
Near one extreme would be pear trees. Along pear stems grow stubby growths, called “spurs,” which bear the tree’s flowers and fruits.

Young pear spur

Older pear spur
These stubby growths grow only an inch or less each year. Over time, spurs branch and these small branches, in turn, branch to create what look like miniature trees perched along the tree’s stems.
A pear’s individual spur can remain vibrant for about a decade, so little pruning is needed annually. But eventually, even a spur grows old and decrepit. I renewal prune my pears by cutting back some of the stubby parts of a spur system to coax out younger stubby growths or even by lopping back a whole stem on which they sit, stimulating new stem growth on which will develop new spurs.
Near the other extreme in pruning would be an everbearing raspberry plant, which bears flowers and fruits on young shoots arising from ground level. Those bearing stems are very short lived. One way to prune an everbearing raspberry plant would be to lop all stems to the ground each winter. Having borne, those stems are aging rapidly, and pruning stimulates a flush of new, bearing stems that will come up from ground level in spring.
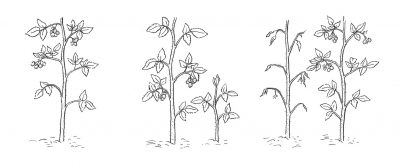
Everbearing raspberry growth habit
(Not to muddy the waters, but everbearing raspberry stems actually bear late in their first summer of growth, then again in midsummer the following year, so stems could be left one more season to bear that second crop. After that, though, the two-year-old stems need to be cut back. They die after their second year anyway.)
Pear and everbearing raspberry represent two extremes in bearing habit and, hence, method of renewal pruning. Other plants lie somewhere on the spectrum between these extremes. Where? It depends, as I wrote, on their particular bearing habit. For instance, blueberry stems are most productive on stems up to 6 years old, gooseberries on stems 2 and 3 years old, and grapes and peaches on stems one year old. So I cut away stems older than 6 years old from my blueberry bushes, stems older than 3 years old from my gooseberry bushes, and stems older than a year old from my grape vines and peach trees.
For other plants grown for either their flowers or their fruits, find out how to renewal prune them by watching how they bear for a season or more, or get the information from a book (such as my book, The Pruning Book).
A Workshop
If you’re interested in delving deeper into pruning, I will be holding a pruning workshop here on my farmden in New Paltz, NY on March 28, 2020. For more information about this workshop, please go to https://leereich.com/workshops.
Not Forgetting the Flowers
Flowers are at a premium this time of year. Here on my farmden, the only flowers blooming outdoors are winter aconite and snowdrops.

Winter aconite
(Typically, my ‘Arnold’s Promise’ witch hazel would be bursting into bloom about now but a few years ago I performed dramatic renewal pruning to reduce the size of the plant. No special technique was involved other than lopping the whole plant to ground level. Witch hazel’s stems bear flowers for many, many years, so don’t need regular pruning; it does take a few years, though before stems are old enough to begin bearing.)
Indoors, plants sense the lengthening days of brightening sunlight. African violets have been blooming for a couple of weeks and will go on doing so for weeks to come.

The same goes for the Odontoglossum pulchellum orchid, whose stems are weighed down with small waxy white, fragrant flowers.
One surprise was a butterfly bush that was in a large pot that I had brought indoors for winter. This plant enjoys bright sun and hot days, neither of which it receives indoors — it has, nonetheless, managed to cough forth, so far, a singe blue blossom. I stick my nose into the flowers, close my eyes, and inhale, and it’s midsummer.

Butterfly bush, indoors
Most dramatic are the humongous, fire engine red bloom of an amaryllis plant. It is gaudy, but appreciated anyway.
My favorites are the white blossoms now opening on Meyer lemon. The blossoms aren’t all that showy but their fragrance is heady and heavenly. No need even to get my nose up close.
I did catch one other bit of welcome color outdoors: my first sighting of bluebirds. The day is gray but the bluebird, to quote Thoreau, was “carrying the [blue] sky on its back.“

