THE TRUTH ABOUT RAIN
/3 Comments/in Gardening/by Lee ReichPlenty of Water Here. Really?
During an entire year, a meager three-hundredths of an inch of rain falls on Arica, Chile, yet halfway across the Pacific in the Hawaiian Archipelago, Mount Waialeale receives a sopping 460 inches. The climate on my farmden, and throughout northeastern U.S., is more or less congenial for growing plants — at least those plants we enjoy in our gardens.
We average about four inches of rainfall each month throughout the year, and this amount complements nicely the inch depth of water per week recommended for most garden plants. Read more
TWO FREE PRUNING TOOLS!
/9 Comments/in Gardening, Tools/by Lee ReichTool Number One
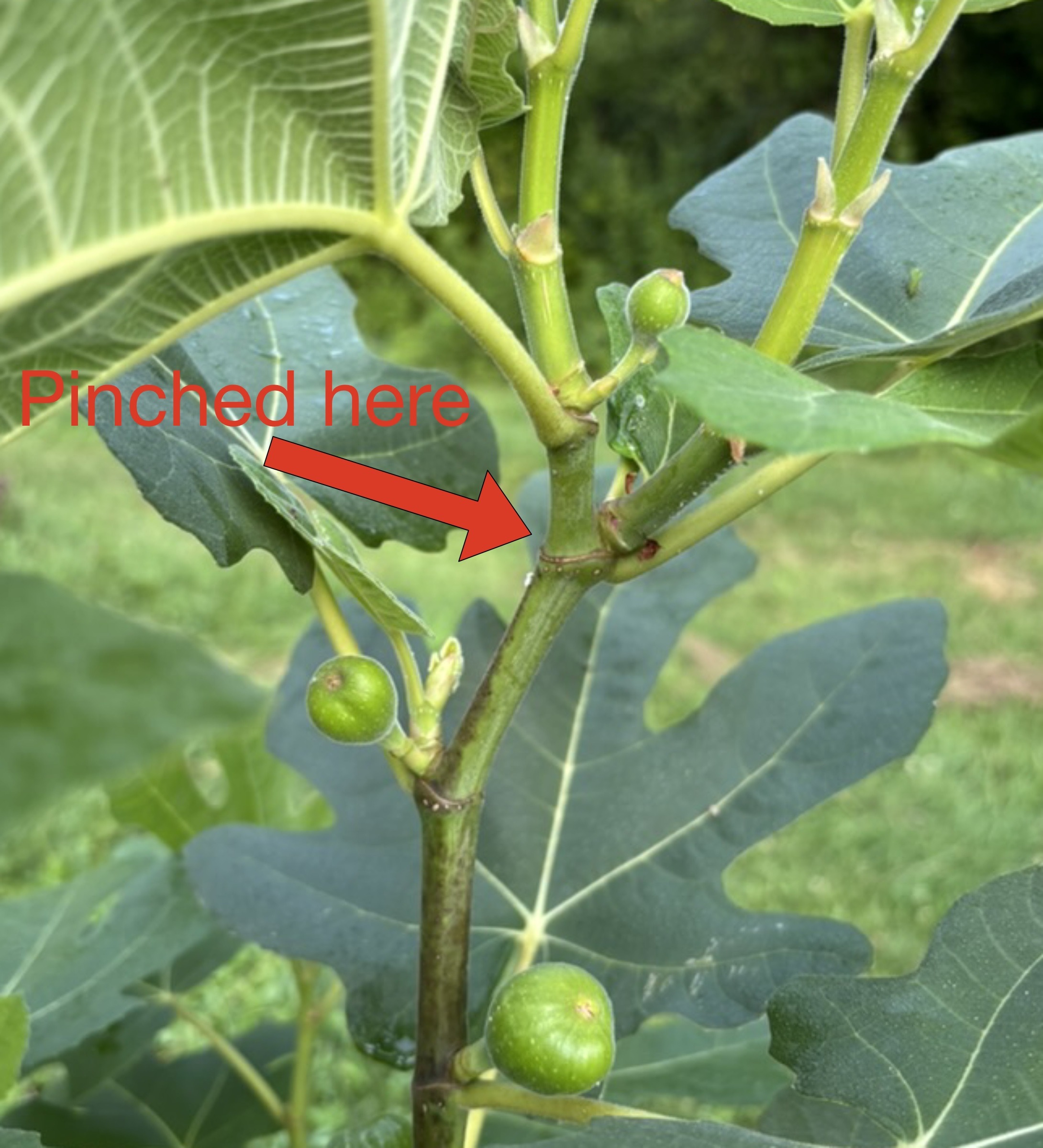
Right now, I have before me a most useful pruning tool, two different kinds of pruning tools, in fact. And they are always with me, even when I sleep. Let’s start with the first: my hands.
I use my hands to rip unwanted stems from plants. This seemingly brutal method of pruning can sometimes do a better job and leave the plant healthier than can a precision cut with pruning shears, even fancy pruning shears. Hand pruning is the best way to get rid of suckers, those overly exuberant, usually vertical stems.
On apple trees, watersprouts poking up along branches are not fruitful, at least not for a few years. Read more
CURE ALL OR SNAKE OIL?
/3 Comments/in Gardening/by Lee ReichMany Uses for Marigold
Gardeners who visit here frequently comment, upon seeing marigold plants growing in and at the foot of my vegetable beds, that I must have planted them for pest control. After all, marigolds are supposed to be one of the workhorses of biological pest control. Plant them and plant pests will be killed or — if they are lucky — merely repelled.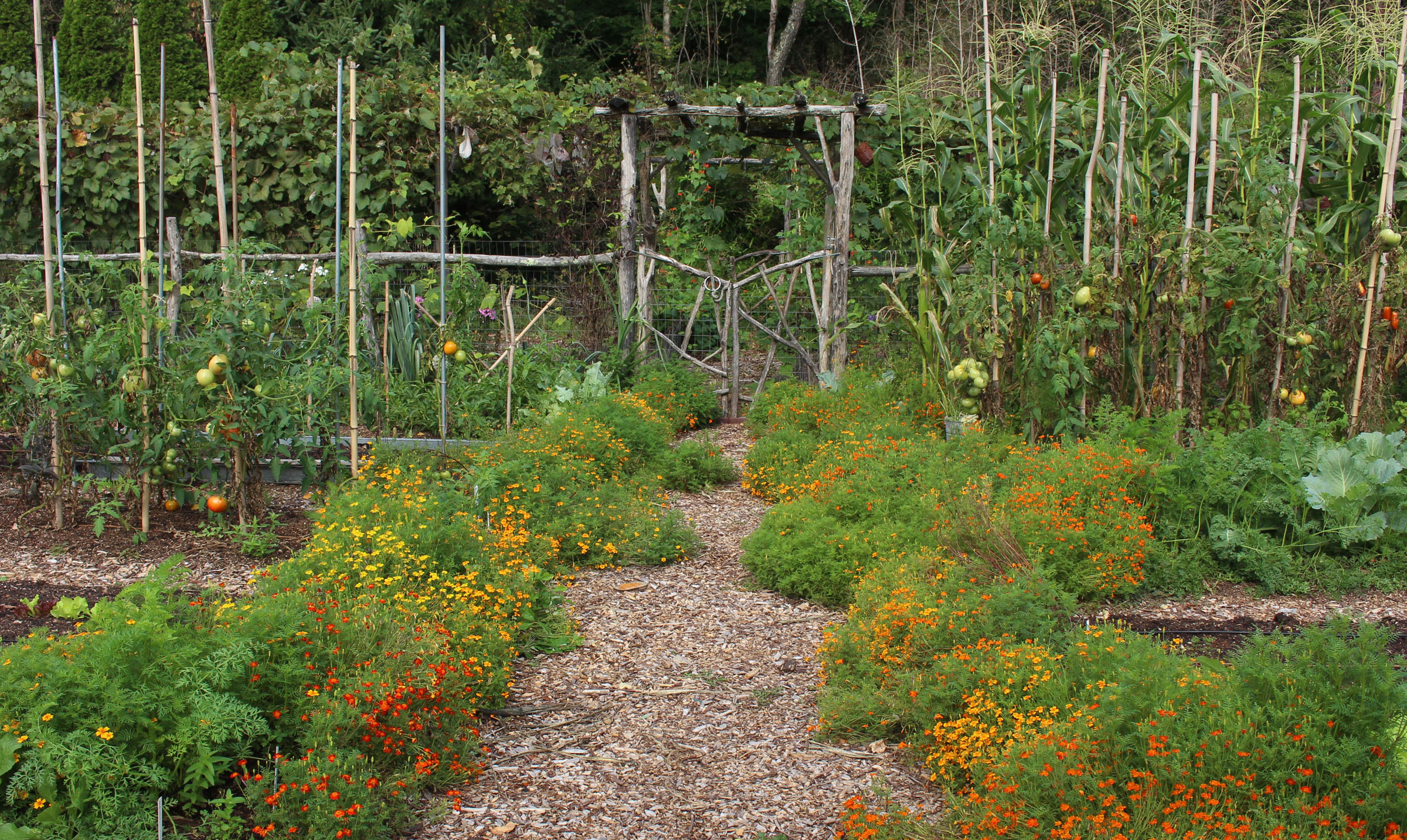
It’s an appealing concept: sunny plants that thwart pestilence and blight even as they brighten the garden with their blossoms. Marigolds greatest claim to pest control fame is their effect on nematodes, an effect documented in numerous scientific studies. Read more