EDEN’S GARDENS
Eden’s Start with Good Soil
G, as I’ll refer to him, has a blank canvas, about 10 acres of mostly open field. His vision is, essentially, for a Garden of Eden, with fruit trees, bushes, and vines, vegetables, nut trees, and flowers. Before he even thought about digging his first planting hole, I suggested he learn something about the soil beneath his blank canvas.
Your and my tax dollars have contributed to a most useful soil resource for G (and you and me), the Soil Web Survey, put out by the Natural Resource Conservation Service (NRCS) of the USDA. This survey provides soils maps of more than 95% of the counties in the U.S., each map delineating what lurks beneath the surface.
Web Soil Survey, opening page
Soils are distinctive, as different from one another as robins are from blue jays. These differences are harder to appreciate, of course, because soil is mostly underground, hidden from view. But if you were to dig some holes a few feet deep and then look carefully at their inside surfaces, you would find that soils are made up of layers of varying thicknesses — called horizons. And one soil might differ from the next not only in the thicknesses of its various horizons, but also in just how the various horizons look and feel. There might be horizons as white as chalk, as red as rust, or as dark brown as chocolate. A horizon might be cement hard, gritty with sand, or stuff for sculpture. And if you were to tease the dirt along one edge of the hole so it falls away naturally — wow! — each horizon would reveal its particles clumped together in such arrangements as plates, blocks, or prisms. Such information, and more, has allowed soils to be classified, much as birds, flowers, and living things are.
Armed with this information, G can know what will thrive in his future paradise and what might need to be done to better accommodate what he wants to grow.
Tax Dollars at Work
The Web Soil Survey is an easy-to-use online resource. Either google it or go directly to http://websoilsurvey.sc.egov.usda.gov/App/HomePage.htm. The big green button labelled “START WSS” gets you started.
The first step is to define your “Area of Interest (AOI)”, that is, your own back forty. Reading down from the AOI tab, you come to the “Address” line, in which, after clicking, you can fill in your own street address. Hit “Return” and, to the right, you’re zoomed into an aerial photo centered on the specified address. Click on one of the two boxes labelled “AOI” (which one depends on whether your AOI is going to be a rectangle or a random polygon) just above the map to delineate, in red, your AOI. Double click the last point and the map enlarges around the defined area.
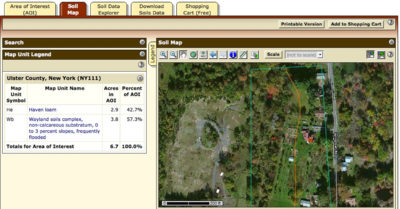
Area of Interest defined
Back to the tabs at the top of the screen, and click on “Soil Map.” Now you know what to call your soil. Yes, its name. If more that one soil exists within the AOI, squiggly lines will delineate their names and extent.
From there, all sorts of useful and not so useful (for you) information are at your fingertips. Click on the soil name and you get a slew of information on that soil, including the all-important drainage class, depth to a restrictive layer, depth to water table, and its ability to hold onto water. Other clicks get you to the soil’s potential use for recreation, construction materials, building site, even military operations.
Most important is soil depth and drainage. G’s is fine, facilitating his first step towards Eden.
A Tree of Eden
Speaking of Gardens of Eden reminds me of fruit and western Asia. Which brings us to a mulberry now ripening in a pot sitting on my front terrace. This mulberry is quite different from those trees now ripening their fruit practically every few hundred feet around here.

Pakistan mulberry fruit
For one thing, this mulberry comes from western Asia, Islamabad, Pakistan, so is not cold-hardy here in New York’s Hudson Valley. Hence the pot, in which the plant resides during winter in my basement, along with figs, pomegranates, and other subtropicals.
The hardy mulberry trees that pop up here and there throughout most cold regions of the U.S. include Asian white mulberries (Morus alba) and out native red mulberries (M. rubra), and their natural hybrids. Note that fruit color has nothing to do with the species. White mulberry is a very variable species, in hardiness, fruit color and flavor, even leaf shape.
Pakistan mulberry is also unique for the size of the berries. Each is a couple of inches long. In warmer climates, the berry can elongate to over 3 inches.

Pakistan mulberry tree in pot
I wouldn’t trouble myself with a potted fruit tree just because it’s exotic and large-fruited; the flavor makes the effort worthwhile. They have a heavenly flavor, among the most delicious of all mulberries, on a par with the world’s best fruits: a rich berry flavor fronting a congenial background of sweetness offset with just the right amount of tartness.
Pakistan is sometimes listed as a variety of white mulberry, other times as a variety of yet another mulberry species, M. macroura. Outdoors, it can grow to 60 feet. In my Garden of Eden, the potted tree will be restrained to 5 or 6 feet.

