MYCO-WHAT?
It’s Greek To Me (and You)
This far north, there’s only a little to do garden-wise this time of year, so let’s sit back and ponder the wonders of plant life. Mycorrhiza, to be specific. Wait! Don’t stop reading! Sure, the word “mycorrhiza” appears intimidating. But mycorrhiza are important in your garden, in the forest, to your trees and shrubs, maybe even to your houseplants.
First, the pronunciation. Say: my-ko-RY-za. It sounds nicer than it looks.
Now let’s take the word apart to see what it means. “Myco” comes from the Greek word meaning “fungus” and “rhiza” from the word meaning “root.” Mycorrhiza, then, is a “fungus-root,” an association between a plant root and a fungus so intimate that the pair has been given a name as if it was a single organism.
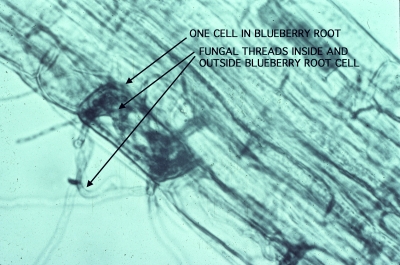
Mycorrhizal blueberry root
Win-Win
The association is symbiotic, beneficial to both parties. One end of the fungus infects a plant root, while the rest of the long, threadlike body of the fungus ramifies through the soil. Nutrients are absorbed from the soil by those fine fungal threads and pumped back to the plant. The result: mycorrhizal plants can draw nutrients and water from a greater volume of soil than can non-mycorrhizal plants, and plant nutrition is improved. To cite one practical demonstration of this benefit, agricultural scientists in California found that the presence of mycorrhiza was equivalent to the addition of more than one hundred pounds of phosphorus fertilizer per acre on citrus trees.
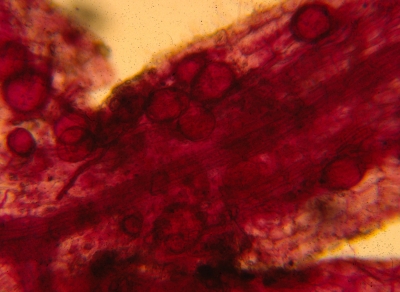
Another kind of mycorrhiza, in apple root
The mycorrhizal association might be termed a balanced parasitism; the fungus does exact payment for its services. Carbohydrates are, literally, the fuel of life, and though mycorrhizal fungi are adept at drawing minerals from the soil, they can’t make their own carbohydrates. So these fungi draw carbohydrates from their host plants, who can make it. Sunlight fuels the photosynthetic reaction of carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates and oxygen.
Not all fungi are mycorrhizal. Non-mycorrhizal fungi get their carbohydrates either by eating living things without returning the favor, in which case they are called parasites. Others eat once-living organisms such as wood, leaves, and dead animals, in which case the fungi are called saprophytes. Some fungi feed on either or both the living and the dead.
Myco-where?
Mycorrhiza are almost ubiquitous on the earth. Walk through the woods in spring or fall and most of the mushrooms you see on the forest floor are the reproductive structures of mycorrhizal fungi, periodically popping up through the ground to spread spores. Below ground, these mushrooms are connected to nearby tree roots by fine fungal threads.
The plant known as Indian Pipes (Monotropa uniflora) offers an eerie signal of the presence of mycorrhizae below ground. This plant, with one nodding flower, is thoroughly white, lacking any chlorophyll with which it could use sunlight to fuel its growth. Instead, its roots tap into a specific mycorrhizal fungus whose underground threads are also tapped into the roots of a nearby tree. Indian pipes is a parasite; it takes from the fungus and the tree, offering nothing in return.

Indian pipes
Mushrooms are formed only by certain types of mycorrhizal fungi. Most mycorrhizal fungi are not so obvious, working unobtrusively in association with the roots of the vegetables and flowers in your garden, your lawn, shrubs, and trees. The gourmet’s truffle is the underground reproductive structure of one type of mycorrhizal fungus.
Most plants on our planet are infected with mycorrhizal fungi. Mycorrhiza are absent only in special situations such as in the acidic, nutrient-poor spoils left from mining operations, in agricultural soils that have been sterilized to kill pests, and in sterilized potting soil in flower pots. Certain plants never become infected; cabbage, spinach, buckwheat, and their relatives, for example.
The Practical Side
The importance of mycorrhiza is not diminished by their ubiquity. Mycorrhiza is a general term, and not all mycorrhiza are equal. A plant may be mycorrhizal, but perhaps not with the most effective species of mycorrhizal fungus or, perhaps, not enough of them. Mulching, fertilization, irrigation, chemical use and other gardening and agricultural practices alter the types and amounts of mycorrhizal fungi in the soil. Rototilling or turning over the ground, as you might imagine, disrupts those fungal threads. Except for high fertility, what’s good for plants — plenty of soil organic matter, growing plants, good aeration, adequate moisture — is also generally good for mycorrhizae.
Old-time gardeners would throw a handful of soil from an old apple tree into the planting hole for a new apple tree. A crude form of mycorrhizal inoculation? Agricultural researchers have tried to quantify why plants respond to inoculation with mycorrhizal fungi at one site, and not another. Which are the best fungi? What affects them? Recent research has shown that improved nutrition is only the most obvious effect of mycorrhiza. The mycorrhizal association also influences plant response to stresses such as drought, insects, and diseases.
As you might imagine, mycorrhizal fungi have been commercialized, available as inoculants or premixed into packaged potting soils. Under certain conditions, this might be beneficial. In many situations, it’s like “taking coals to Newcastle.” Usually, create conditions conducive to mycorrhizal formation, and a beneficial symbiosis will develop.
For my research as a graduate student, I studied the effect of, among other things, mycorrhizae in blueberry soils. Even my plants grown in sterilized soils in a greenhouse became mycorrhizal, which, while messing up that aspect of my experiment, did highlight how ubiquitous the association can be without the human hand.
If you want to lend your hand to the mycorrhizal association, you could actually extract and grow your own mycorrhizal inoculum. Read how, and learn all about mycorrhizae in Jeff Lowenfels’ excellent book Teaming with Fungi: The Organic Grower’s Guide to Mycorrhizae.
At any rate, mycorrhiza is a fascinating demonstration of ecology, the interrelationship of organisms on the earth.



Dear Lee,
What a great, lucid essay on myccorhiza. I finally get it. Thank you so much.
Questions– perhaps you have talked about this in a previous blog but what are your favorite sources for blueberries and other berries like lingonbery? Most of our work is in Fairfield County.
Thanks, Lee.
Wendy
I usually get those from Raintree Nursery (see their banner ad on my blog page). They’re in the Pacific NW, but named varieties of fruits are clonally propagated so if a variety will grow well at your site, the plants will be equally well adapted no matter where they were propagated.
Hi again,Lee,
Never mind my request for berry sources. I remembered that I have your great book, ‘Uncommon Fruits’, and of course you have sources in the appendix.
Wendy
Happy hunting and planting.
I found an Indan pipe in the woods, I wanted to take it but I know they will not live if moved away from the mycorrhizal fungus.
Besided it is bad form to move wild plants.
All true.
Your explanation is very helpful for so many reasons, including teaching me to properly pronounce mycorrhiza.
Is it true that most lawns have less mycorrhizae than land planted with perennials, shrubs and trees? If so, is there a remedy?
I continue to be grateful for your books and newsletters. I’ve studied and relied on them for decades.
Jane
No, not true that there is less mycorrhizae in lawns. Where did you come across that non-fact?
An arborist told me a while back that a tree growing in a lawn will benefit from mulching, partly to increase the fungal activity.
They will benefit from mulch but that “to increase the fungal activity” is popular thinking these days but a stretch of reality. Mulch has many benefits.
Thanks for letting me know. So interesting.
You note that cabbages do not become infected with the mycorrhizal fungi. Are all brassicas resistant to the assistance of the fungi and if they are is there any advantage to maintaining a “no dig” bed for them?
Yes, that’s true of all brassicas. There are many other advantages of “no dig” (as I spell out in my book WEEDLESS GARDENING) in addition to not disturbing mycorrhizal fungi.
Hi Lee: thanks for the completest article I have yet read on Mycorrhizae. I so wish I could learn how to spell it without needing to look it up every time! But if the fungi are added to pre-packaged potting soils, how long will they live in sealed plastic bags away from the plants they partner with?
Thanks,
Kari, MN
Some kinds of mycorrhiza form spores that should survive even in plastic bags.
If Lee says read it, I’ll read it.
Would you have a recommendation for a readable book on the broader aspects of soil science? I live in the West, on what must be one of the world’s biggest lumps of clay. I’ve been pilling on the compost, but it is slow going. With no rain in the summer, the ground becomes brick hard, and there are no earthworms or other creatures in the soil to incorporate the compost. Raised beds are an answer, but then there’s the problem of how to get the soil in the raised bed to mimic the desired naturally occurring soil. I need help, any suggestions?
For very in-depth soil science, I like THE NATURE AND PROPERTIES OF SOIL by Brady and Wiel. Also good, but somewhat outdated, is “Fundamentals of Soil Science” by Foth and Turk. No-till isn’t a religion: You might try a one time digging in of abundant compost, even sawdust (as I recommend in WEEDLESS GARDENING), into your soil and then forming beds. Drip irrigation would also help things along.
Great article – super interesting
Thanks.
Lee-
Thanks for the post and I love your book Uncommon Fruits for Every Garden. Many nurseries sell mycorrhiza inoculant packs to place on bare roots upon planting. I’ve tried them with mixed success. Any thoughts on if these work better than the natural process?
Glad you like my book. It’s currently out of print but will be re-issued within a couple of years, updated and with some surprising additions.
I would not buy the mycorrhizal innoculants. They might be of benefit if your soil lacked suitable mycorrhizal fungi; and if the bought innoculant was better suited to your soil, environment, and plants than your native mycorrhizal fungi. Probably no benefit.